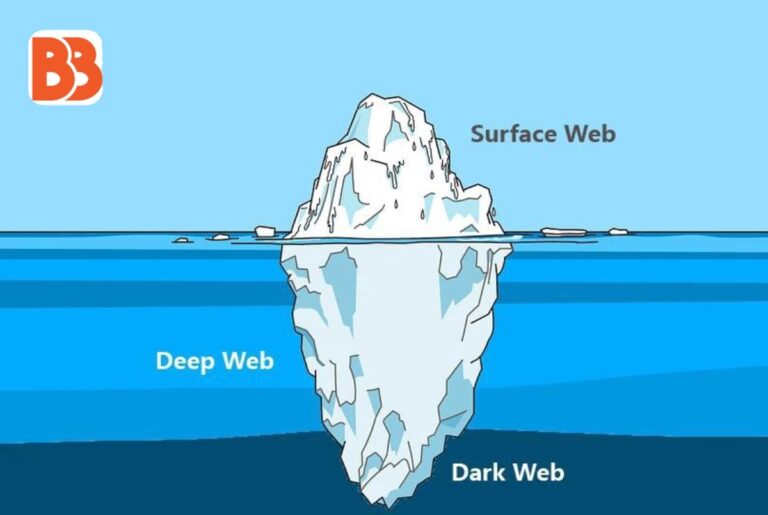
The internet is a vast network, but what we access through search engines like Google represents just a tiny portion of the whole. The terms “Deep Web vs Dark Web” are often misunderstood, leading to confusion about their roles in the online ecosystem. While they both exist outside the easily searchable surface web, they serve vastly different functions. Understanding their differences is crucial for grasping how the internet operates beyond the scope of common search engines.
Understanding the Deep Web
The Deep Web constitutes the majority of the internet, making up over 90% of online content. Unlike the surface web, which search engines index and present to users, the Deep Web contains web pages and content. That are not accessible via standard search engines. However, the Deep Web is not as mysterious or dangerous as it may seem. Rather, it includes everyday online activities that are kept private for security reasons.
Examples of the Deep Web include:
- Online banking portals: Accessing your account and financial data falls within the Deep Web because only you, with proper authentication, can view your account.
- Medical records: Personal medical histories and hospital databases, which are password-protected and kept private, are also stored in this part of the web.
- Subscription services: Paid academic journals, research papers, and streaming services often require a subscription or login, putting them beyond the reach of general search engines.
- Corporate databases: Company files, internal communications, and other sensitive business data are stored securely in the Deep Web.
Purpose and Use Cases of the Deep Web
The Deep Web is a crucial part of the digital infrastructure. It provides secure access to information, ensuring that sensitive or private data remains protected. For instance, universities store vast databases of research articles, libraries maintain vast catalogues. And corporations store proprietary documents in secure databases accessible only by authorized personnel.
For the average internet user, the Deep Web is a functional part of daily life. Whether logging into an email account, conducting online banking, or shopping, users are regularly interacting with the Deep Web. This layer of the web allows for seamless, secure interactions online, ensuring that sensitive data. Such as personal information or credit card details, remain safe.
What is the Dark Web?
The Dark Web is a small subset of the Deep Web, deliberately hidden and accessible only through specialized software like Tor (The Onion Router). Tor helps users access this part of the web by routing internet traffic through multiple servers. Making it difficult for anyone to trace the user’s activities or IP address. The Dark Web is renowned for its anonymity, which has led to its association with illicit activities, but this reputation only captures part of the picture.
Legitimate Uses of the Dark Web
- Whistleblowing: Tools like SecureDrop allow whistleblowers to submit confidential information to journalists anonymously.
- Political activism: In countries with oppressive regimes, activists use the Dark Web to organize and communicate safely without government interference.
- Private communications: Journalists and political dissidents use the Dark Web to communicate in environments where privacy is compromised.
Misconceptions About the Dark Web
While illegal activities do occur on the Dark Web, not everything found there is unlawful. It’s important to differentiate between the Dark Web’s tools for legitimate privacy purposes and the illicit trade or criminal activities also present there. Platforms like SecureDrop have revolutionized the way whistleblowers and journalists interact. Providing a secure platform for exchanging sensitive information.
Key Differences Between the Deep Web and Dark Web
Accessibility
The most significant difference between the Deep Web and Dark Web lies in how users access them:
- Deep Web: Most content here is password-protected and not indexed by search engines but accessible with proper login credentials.
- Dark Web: Requires specialized software like Tor, designed specifically for anonymity and encryption, making it more difficult to access.
Purpose
The Deep Web and Dark Web also serve different purposes:
- Deep Web: Facilitates secure, legitimate access to personal and corporate data, such as academic databases or online banking.
- Dark Web: Provides an anonymous, encrypted space, often used for both legal and illegal activities, such as anonymous communication, activism, or criminal transactions.
Size
- Deep Web: Comprises the vast majority of the internet, including countless private databases, password-protected services, and other secure areas.
- Dark Web: Represents only a small portion of the Deep Web, with estimates ranging from 5% to 10% of total internet content.
The Role of Technology: Encryption and Anonymity
Both the Deep Web and Dark Web rely heavily on encryption and secure technologies to keep their content private. In the Deep Web, encryption protocols like HTTPS and VPNs are essential for protecting user data from hackers and cybercriminals. On the Dark Web, tools like Tor are used not just for privacy but also for anonymity.You can also learn about “The Role of AI in Policing Dark Web Activities“.
Tor works by bouncing internet traffic through multiple servers across the world, disguising the user’s IP address and making it almost impossible for any third party to track their activities. This level of anonymity has given the Dark Web its reputation as a hub for illegal transactions. But it’s also a valuable resource for those living under surveillance-heavy regimes.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Deep Web vs. Dark Web while the Deep Web is essential for online security, the Dark Web raises more complex legal and ethical questions. Law enforcement agencies across the world struggle to regulate the Dark Web due to its inherently anonymous and encrypted nature. The sale of illicit goods like drugs, firearms, and fake identification is rampant on the Dark Web. Which often hosts marketplaces that operate similarly to online shopping platforms.
However, law enforcement agencies have had some success infiltrating and taking down criminal enterprises on the Dark Web. Such as the 2013 shutdown of the infamous Silk Road, a black market for illegal drugs. Despite these successes, the difficulty of tracing users and transactions on the Dark Web means that it remains a largely lawless space. Where crime is both rampant and difficult to prosecute.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
In an era where privacy concerns and cybersecurity threats dominate the news, understanding the difference between the Deep Web and Dark Web is crucial for internet users. While the Deep Web plays a necessary role in protecting personal and sensitive data. The Dark Web raises questions about the balance between privacy, anonymity, and legality.
As more people become aware of the risks and opportunities associated with both parts of the web, it becomes clear. That technologies like encryption and anonymity have both positive and negative implications. For some, these technologies provide essential protections, while for others, they offer a way to exploit the internet’s anonymity for criminal purposes.
Conclusion
The Deep Web vs Dark Web represent two distinct but interconnected layers of the internet. The Deep Web is a vital part of daily online activity, providing security and privacy for legitimate purposes. Like banking, academia, and personal communication. The Dark Web, by contrast, is more controversial, offering anonymity that can be used for both positive and negative ends.
Understanding the differences between these two parts of the web is critical for staying informed about how online privacy, security, and anonymity are evolving in an increasingly digital world. Whether you’re conducting research in the Deep Web or learning about the ethical complexities of the Dark Web. Knowledge is key to navigating these hidden layers of the internet responsibly.